3D elastic seismic modelling with surface topography
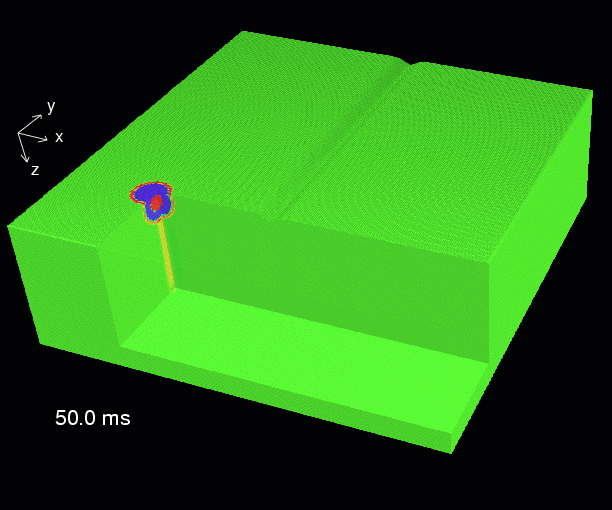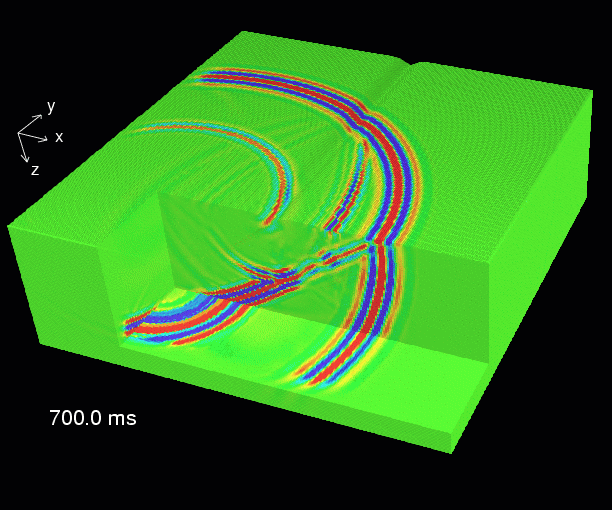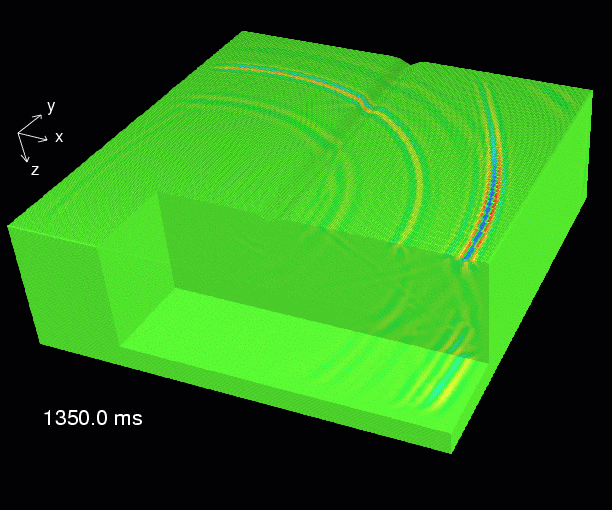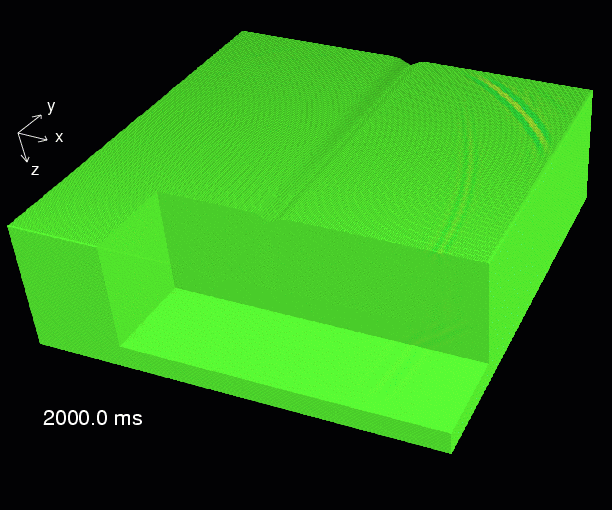
This is an example of a 3-dimensional numerical elastic simulation. The table shows the modelling parameters. The animation shows a series of snapshot blocks 50 ms apart. The snapshots display the total particle velocity.
The material parameters are those of a homogeneous isotropic medium. There is a trench-like surface topography with a maximum depth of 35 m. The trench axis follows the y-direction.
Model parameters
| nx | 225 |
| ny | 225 |
| nz | 81 |
| delta_x | 10 m |
| delta_y | 10 m |
| delta_z | 10 m |
| delta_t | 1 ms |
| t_max | 2 s |
| f_max | 35 Hz |
| vp | 2000 m/s |
| vs | 1155 m/s |
| rho | 1000 kg/m3 |
The source is an explosive source which lies 10 grid points below the surface. It generates a P-wave. A guides S-wave is generated due to conversion at the free surface. Also a Rayleigh wave can be observed.
When the P-wave hits the trench a guided Rayleigh wave and an S-type body wave are generated due to scattering.
Note that the gain is increased with time, so that the P-wave energy at late times is still visible. As a consequence also reflections from the not perfectly absorbing bottom boundary are also visible.
Due to the cyclicity of the DFTs wrap-around effects can be seen at the sides. Since the modelling volume is surrounded by tapering zones waves leaving one edge are sufficiently damped when entering into the modelling grid at the opposite side.
Reference:
Tessmer, E., Kosloff, D.,1994, 3-D elastic modeling with surface topography by a Chebyshev spectral method, Geophysics, 59, 464-473